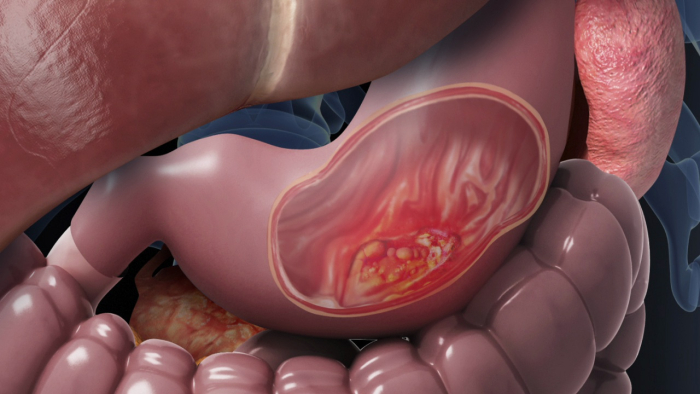
Stomach cancer, also called gastric cancer, is the abnormal growth of cells in the lining of the stomach. It usually develops gradually over many years and can turn into a tumor. It usually grows slowly over many years. It is most common in people in their late 60s to 80s. Almost all stomach cancers (about 95%) start in the glandular tissue that lines the stomach. The tumor may spread along the stomach wall or grow directly through the wall and shed cells into the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Once it leaves the stomach, it can spread to other organs
What causes cancer
Scientists don't know exactly what causes cancer cells to grow in the stomach. But there are a few things that can increase your risk of developing the disease. One of them is infection with a common bacteria called Helicobacter pylori, which causes ulcers. Inflammation of your intestines called gastritis, a type of long-term anemia called pernicious anemia, and abnormal cell growths in the stomach called polyps can also increase your risk of cancer
Signs and symptoms
In the early stages, stomach cancer may not have any specific symptoms. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms may appear
Nausea and vomiting
Heartburn
Indigestion
Feeling bloated after eating
Loss of appetite
Feeling full after eating a small amount of food
Abdominal pain
Feeling very tired
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
As stomach tumors grow, more serious symptoms may occur, such as
Stomach pain
Unexplained weight loss
Trouble swallowing
Yellowing of the eyes or skin
Swelling in the stomach
Constipation or diarrhea
Weakness or feeling tired
Heartburn
Things that seem to contribute to an increased risk of stomach cancer
Smoking
Being overweight or obese
A smoky, pickled, or salty diet
Drinking alcohol regularly
Stomach surgery for ulcers
Working in the coal, metal, wood, or plastic industries
A family history of stomach cancer
Inherited factors such as familial adenomatous polyposis, hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (Linge syndrome), and Patz-Jeghers syndrome
A diet low in fruits and vegetables
Preventive measures
The following measures can be taken to reduce the risk of stomach cancer
Healthy diet: Consume fresh fruits and vegetables, reduce the consumption of salty, smoked and pickled foods
Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of stomach cancer
Weight management: Maintain weight and prevent obesity
Helicobacter pylori infection: This bacteria can increase the risk of stomach cancer
How to deal with stomach cancer
Treatment for stomach cancer depends on the stage and spread of the disease and may include
Surgery: Removing part of the stomach (subtotal gastrectomy) or the entire stomach (total gastrectomy)
Chemotherapy: Using anticancer drugs to shrink the tumor or kill cancer cells
Radiation therapy: Using radiation to kill cancer cells
Immunotherapy: Boosting the body's immune system to fight cancer
Ways to diagnose
To diagnose stomach cancer, your doctor may use the following methods
Endoscopy: In this method, a thin, flexible tube with a small camera is inserted through the mouth into the stomach to obtain detailed images of the inside of the stomach.
Biopsy: If suspicious areas are seen during endoscopy, a sample of tissue is removed for further examination
Imaging tests: Such as CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds to check for the spread of cancer to other organs
Types of stomach cancer
The type of stomach cancer is based on the type of cell where the cancer started
Examples of types of stomach cancer include
. Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma stomach cancer starts in cells that produce mucus. This is the most common type of stomach cancer. Almost all cancers that start in the stomach are gastric adenocarcinomas
. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) start in certain nerve cells found in the stomach wall and other digestive organs. GIST is a type of soft tissue sarcoma
. Carcinoid tumors are cancers that start in nerve cells that make hormones. Neuroendocrine cells are found in many parts of the body. They perform some of the functions of nerve cells and some of the functions of hormone-producing cells. Carcinoid tumors are a type of neuroendocrine tumor
. Lymphoma is a cancer that starts in the cells of the immune system. The body's immune system fights germs. Lymphoma can sometimes start in the stomach. This can happen if the body sends immune system cells to the stomach while the body is trying to fight off an illness. Most lymphomas that start in the stomach are a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Frequently asked questions
What is stomach cancer
Stomach cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the stomach that can spread to other tissues in the body
What causes stomach cancer
Genetic factors, Helicobacter pylori infections, smoking, unhealthy diet, and family history can increase the risk of developing this cancer
What are the symptoms of stomach cancer
Symptoms include indigestion, stomach pain, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and stomach bleeding
Is stomach cancer preventable
Yes, the risk of stomach cancer can be reduced by following a healthy diet, quitting smoking, and treating Helicobacter pylori infections
Who is at higher risk of developing stomach cancer
People over 60, people who smoke, or those with a family history of stomach cancer are at higher risk of developing this cancer
How is stomach cancer diagnosed
Methods such as endoscopy, biopsy, and imaging tests are used for diagnosis
What treatments are available for stomach cancer
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy
Are there any specific foods that are helpful in preventing stomach cancer
Consuming fresh fruits and vegetables, reducing the consumption of salty and smoked foods can be helpful
Is it possible for this disease to spread to other organs in the body
Yes, stomach cancer can metastasize to other organs such as the liver, lungs, and bones
Resources
https://www.webmd.com/cancer/stomach-gastric-cancer
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stomach-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20352438